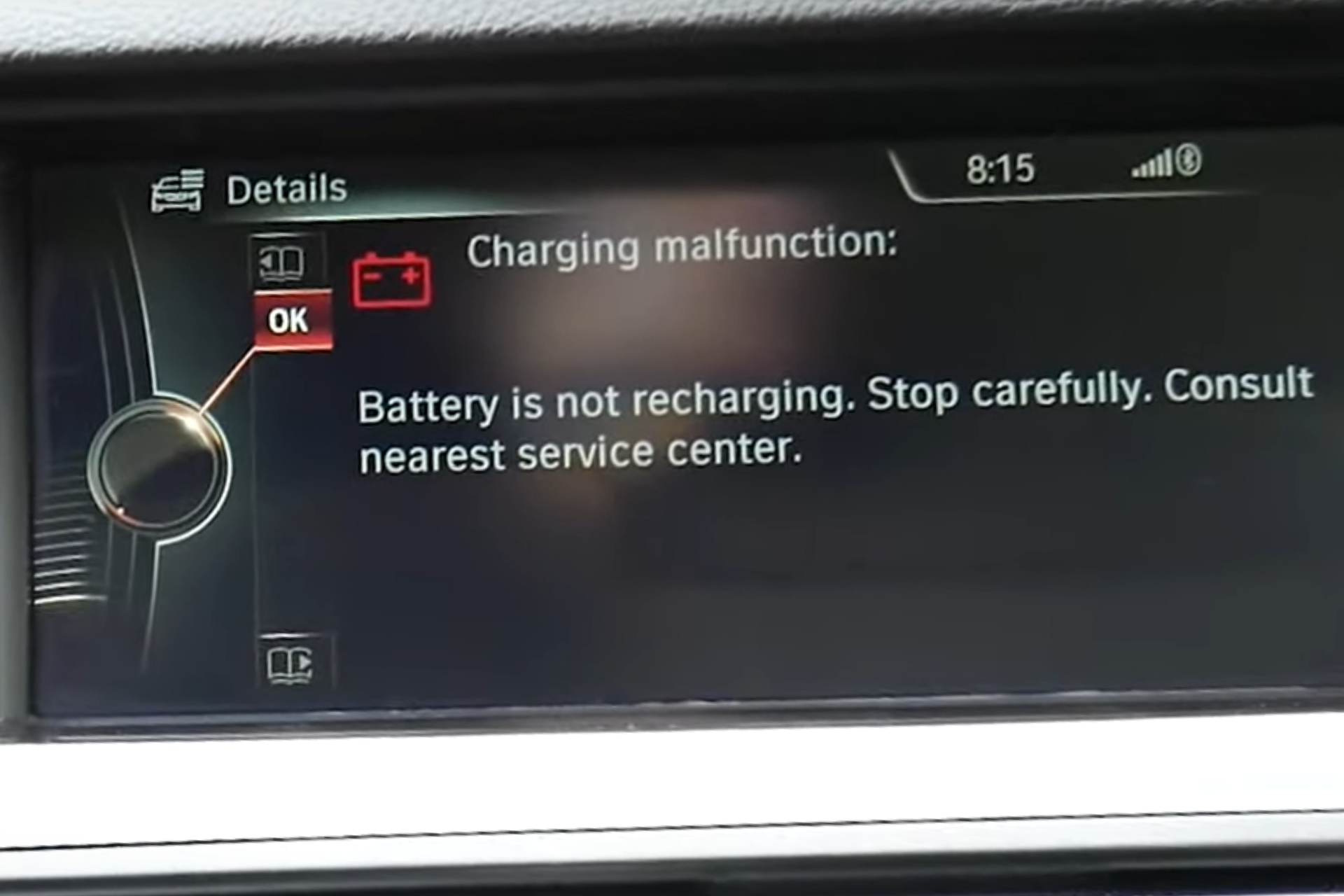
No matter if you drive a BMW 3 Series, 5 Series, or X5, there is a chance that it will develop a charging malfunction, indicated by a battery light on the dashboard.
In this article, we will walk you through the causes of a charging malfunction, how to diagnose and fix these issues, and discuss whether it’s safe to continue driving.
Quick Answer: What is a BMW charging malfunction?
A BMW charging malfunction means that the battery is not being charged while the engine is running. It is most often caused by a faulty alternator or a bad battery.
5 Causes and fixes for a BMW charging malfunction
Here is a list of possible causes for a BMW charging malfunction, sorted from most to least common:
- Faulty alternator.
- Bad battery.
- Snapped or loose auxiliary belt.
- Faulty auxiliary belt tensioner pulley.
- Blown alternator fuse.
- Corroded or loose battery cables and connections.

1. Faulty alternator
One of the most common causes of a BMW charging malfunction is a faulty alternator.
The alternator is responsible for generating electrical power to recharge the battery while the car is running.

When the alternator is not functioning correctly, it does not supply (sufficient) power, leading to a charging malfunction.
After some time, a faulty alternator will also cause a fully depleted battery and, ultimately, a BMW that won’t start.
A faulty alternator can stem from several issues, including worn-out brushes, a failing voltage regulator (which is often integrated into the alternator), damaged bearings, or broken internal wiring.
Diagnosing a faulty alternator
A great way to test if a faulty alternator is the cause of a BMW charging malfunction is to perform a battery voltage test:
- With the engine off, use a voltmeter to check the battery voltage.
- A healthy battery should read around 12.6 volts.
- Start the engine and check again; the voltage should rise to between 13.7 and 14.7 volts, indicating the alternator is charging the battery. If the voltage does not increase, the alternator may be faulty.
Fixing a faulty alternator
If you’ve found that you have a faulty alternator, it’s necessary to replace it as soon as possible.
It’s a task that you can do yourself quite easily. It involves removing the auxiliary belt, loosening the bolts that hold the alternator, and securing the new alternator.
A new BMW alternator costs between $200 and $500.
A BMW dealer will usually charge between $500 and $1,000 for replacing a faulty alternator.
2. Bad battery
Another important component of your BMW’s charging system is the battery, which stores electrical energy to start your engine and power your vehicle’s electronics when the engine is off.
Over time, every battery loses its ability to hold a charge due to age, usage, and exposure to extreme temperatures.
Therefore, a bad or failing battery is a common culprit behind charging malfunctions in BMWs.

Diagnosing a bad battery
BMW batteries typically have a lifespan of 3 to 5 years. If yours is within or beyond this range, it might be time for a replacement.
However, like with the alternator, you can diagnose a bad battery using a multimeter:
- Use a multimeter to measure the battery voltage.
- A fully charged BMW battery should read around 12.6 volts or more when the vehicle is off.
- A reading under 12.4 volts indicates a battery not holding a proper charge.
Fixing a bad battery
Replacing a bad battery is straightforward and can be done with a few tools.
Make sure the new battery matches your BMW’s specifications. The owner’s manual or a quick online search can help you find the right model and size.
In most BMW models, the battery is located in the trunk or under the hood.
Note that when a battery is replaced, it also has to be registered to the car. You can do this using an OBDII tool like OBDeleven.
A BMW battery costs between $100 and $250. A battery replacement at the dealer usually costs between $300 and $400.
3. Snapped or loose auxiliary belt
The auxiliary belt, also known as the serpentine belt, drives the alternator and other components like the air conditioning compressor and the power steering pump.
When this belt snaps or becomes loose, it leads to a charging malfunction because the alternator cannot generate (enough) power to charge the battery.
Diagnosing a snapped or loose auxiliary belt
Diagnosing a snapped auxiliary belt is simple because you can look under the hood to check the condition of the belt.
A BMW auxiliary belt is most often located at the front of the engine. Here is an example of a snapped auxiliary belt:

A loose auxiliary belt is a bit more challenging to diagnose. Here are some common signs:
- Loss of power steering and air conditioning. One of the first signs of a problem with the auxiliary belt is the sudden loss of power steering or air conditioning functionality. This happens because the belt is no longer driving these components.
- Squealing noises. A loose belt may produce a squealing noise, especially on startup or when using power-intensive features like the air conditioning, indicating it’s slipping.
- Check belt tension. If the belt is still intact, press down on it lightly. The belt should have a little give, but too much movement indicates it’s too loose. Most modern BMWs have an automatic tensioner, which means if the belt is loose, the tensioner may be failing. (We will discuss this in the next section.)
A BMW auxiliary or serpentine belt should be replaced every 50,000 to 60,000 miles.
Tip: Note that an auxiliary/serpentine belt is something different than a timing belt or chain.
Fixing a snapped or loose auxiliary belt
A snapped or severely loose auxiliary belt requires immediate attention.
In both cases, it is advised to replace the auxiliary belt, tensioner, and pulley.
These parts are not too expensive, and replacing them all together will ensure you won’t experience this problem for the foreseeable future.
Replacing these parts is possible yourself without using specialized tools. All the parts will cost you about $100. A skilled mechanic will do it in about 20 minutes.
A dealer will charge you between $200 and $500 for this job.
4. Faulty auxiliary belt tensioner
The auxiliary belt tensioner is a component that maintains the correct tension on the auxiliary belt.

A faulty tensioner can lead to a loose or misaligned belt, resulting in a charging malfunction as the alternator cannot generate power efficiently.
Diagnosing a faulty auxiliary belt tensioner
A common symptom of a failing tensioner is a rattling, grinding, or squeaking noise coming from the engine bay, especially when the engine is idling or shortly after the vehicle has been started.
A malfunctioning tensioner can also cause the belt to become misaligned or slip off the pulleys, indicated by uneven belt wear or the belt not sitting correctly on the pulleys.
You can also check for any looseness in the pulley’s bearing by wiggling it back and forth.
Fixing a faulty auxiliary belt tensioner
Like with the previous cause, fixing a faulty auxiliary belt tensioner means replacing the belt, tensioner, and pulley.
This is the same job as for a snapped or loose auxiliary belt.
5. Corroded or loose battery cables and connections
Although uncommon, corrosion, looseness, or damage to battery cables and connections can disrupt the flow of electricity between the battery, alternator, and the vehicle’s electrical system, leading to charging malfunctions and other electrical issues.
Diagnosing corroded or loose battery cables and connections
Here are some ways you can check your BMW’s cables and connections:
- Inspect for physical damage, Conduct a thorough visual and physical examination of the battery terminals, cables, and connections for any signs of corrosion, looseness, or damage.
- Clean corrosion. Use a battery terminal brush or a mixture of baking soda and water to clean off any corrosion from the terminals and cable ends. After cleaning, a clear, metal-to-metal contact should be visible.
- Tighten connections. Ensure that the battery cables are tightly fastened to the terminals. You might need a wrench to tighten the connectors properly.
- Check for continuity and resistance. Using a multimeter, check for continuity in the cables and measure resistance. High resistance or lack of continuity could indicate damaged cables needing replacement.
Fixing corroded or loose battery cables and connections
If you’ve found a loose battery cable or connection, it’s necessary to replace the cable, and replace or clean the connection.
Can you continue driving with a charging malfunction?
Driving with a BMW charging malfunction has significant risks and is not recommended.
When there’s a malfunction, the battery’s reserve power is all that’s left to keep everything running, which can deplete rapidly.
As the battery depletes, you might experience a gradual loss of power to various systems.
Initially, non-essential features like the radio or air conditioning may fail, but eventually, critical systems like the ignition and fuel systems could be affected, leading to the engine shutting off while driving.
Therefore, the most immediate concern is the possibility of the vehicle coming to a complete stop once the battery is fully discharged, potentially stranding you in unsafe or inconvenient locations.
If you must continue driving to reach a safe location, turn off the air conditioning and radio to conserve battery power.
An overview of the BMW charging system
The charging system in your BMW has several key parts:
- Alternator. The alternator converts mechanical energy from the engine’s rotation into electrical energy, which is then used to recharge the battery and power the vehicle’s electrical systems while the engine is running.
- Battery. The battery provides the electrical power necessary to start the engine and powers the vehicle’s electrical accessories when the engine is not running.
- Voltage regulator. Integrated within the alternator in most modern BMWs, the voltage regulator ensures the alternator produces the right amount of voltage to keep the battery charged without overcharging it. It maintains a consistent output, typically between 13.5 and 14.5 volts, to protect the electrical components and battery.
- Auxiliary belt (serpentine belt). This belt transfers mechanical power from the engine’s crankshaft pulley to the alternator, allowing it to generate electricity. It also drives other components, such as the air conditioning compressor and power steering pump.
- Fuses and wiring. The electrical wiring in your BMW connects the charging system components, while fuses protect the system from overcurrents that could damage the electrical components.
When you start your BMW, the battery provides the initial power needed to turn the engine over. Once the engine is running, the alternator takes over as the primary source of electrical power.
The alternator generates alternating current (AC) electricity, which is converted into direct current (DC) electricity that the vehicle’s systems can use.
The auxiliary belt ensures that the alternator is driven consistently by the engine’s rotation.
Conclusion
I hope this article has helped you find the causes and fixes for your BMW charging malfunction.
If you have any experience with this issue, let everyone know in the comments below!